

Metallurgical evaluation plays a crucial role in modern engineering, verifying that metals can meet demanding standards of strength and reliability. Whether in aviation, construction, or heavy industry, these tests provide assurance that materials will endure tough environments and long-term usage.
Metallurgical evaluation plays a crucial role in modern engineering, verifying that metals can meet demanding standards of strength and reliability. Whether in aviation, construction, or heavy industry, these tests provide assurance that materials will endure tough environments and long-term usage.
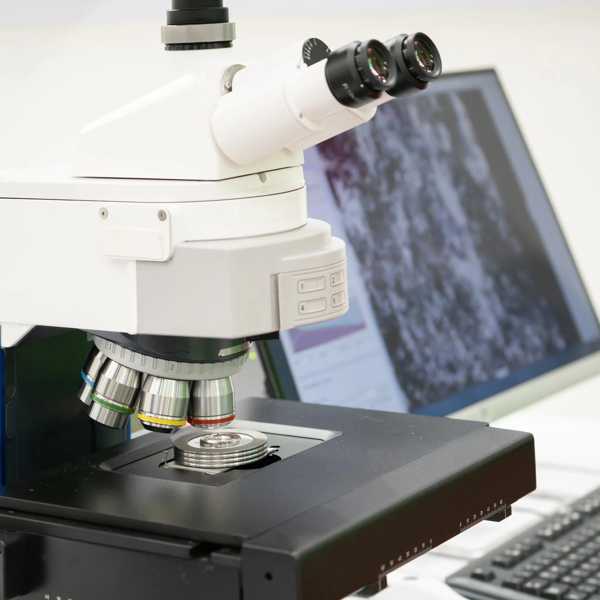
Metallurgical testing examines both the physical and chemical characteristics of metals to ensure compliance with technical and safety regulations. By identifying weaknesses early, it reduces failure risks, enhances performance, and safeguards users in applications such as infrastructure, vehicles, and aircraft.
Key sectors—including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and civil engineering—rely heavily on metallurgical assessments. These evaluations validate material suitability, predict durability, and confirm adherence to compliance standards, helping organizations avoid costly recalls or design revisions.
A complete metallurgical testing framework incorporates advanced tools and methods such as tensile testers, spectrometers, metallographic microscopes, sample preparation units, and fully equipped laboratories. Together, these instruments generate reliable data for verifying material performance.
Spectrometers for Steel and Alloys
Analyze elemental composition to confirm alloy consistency and quality.
Mechanical and Structural Assessments
Hardness checks, fatigue studies, and microscopic imaging determine strength, wear resistance, and structural integrity.
Polishing Systems
Prepare high-quality surfaces for microscopic examination, ensuring accurate detection of flaws.
Comprehensive Lab Equipment
Furnaces, hardness testers, and metallurgical microscopes enable complete evaluation of material properties.
Tensile Testing Machines
Measure ductility, elasticity, and ultimate strength by applying controlled force until deformation occurs.
Metallurgical Accounting Solutions
Track raw material use across production, improving efficiency and minimizing waste.
Professional Laboratory Services
Independent labs provide compliance certification, full validation, and impartial results.
Routine Quality Checks
Ongoing inspections confirm adherence to industry standards and detect issues early.
Regional Laboratories
Offer convenient access, faster results, and services like defect detection, certification, and compliance checks.
MTS Metallurgical Services
A leading provider in aerospace and automotive industries, MTS specializes in advanced strength, durability, and environmental resistance testing, backed by cutting-edge equipment.
| Equipment | Purpose | Features | Ideal Use Case |
| Spectrometer | Determines composition | High precision, fast results | Alloy validation, quality control |
| Tensile Tester | Tests elasticity/strength | Force-controlled measurements | Stress analysis, R&D |
| Polishing Unit | Sample preparation | Adjustable polishing intensity | Microstructure & defect investigation |
Automation & AI – Automated systems and machine learning enhance accuracy, reduce human error, and speed up analysis.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) – Techniques such as ultrasonic and radiographic scanning allow thorough inspection without damaging materials.
Sustainable Testing Practices – New eco-conscious approaches aim to reduce waste and energy use while maintaining precision.
Q: What is the primary purpose of metallurgical testing?
A: To verify that metals meet critical safety, durability, and compliance requirements.
Q: How does a spectrometer function?
A: It identifies the exact elemental composition by analyzing light spectra emitted from a sample.
Q: Which industries rely most on these systems?
A: Aerospace, automotive, civil construction, and advanced manufacturing.
Q: Are tests always conducted in labs?
A: While many evaluations occur in labs, some can be performed on-site, depending on the method.
Q: Can professionals train in metallurgical testing?
A: Yes—universities, technical schools, and industry groups provide training and hands-on courses.
Metallurgical testing remains the backbone of metal quality assurance, ensuring reliability, safety, and long-term performance. With innovations in automation, AI, and environmentally friendly practices, testing systems are becoming more efficient and precise—driving forward both industrial safety and material innovation.