

Plaque psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disease characterized by the formation of red, raised, and scaly patches on the skin. These spots, also called plaques, can appear anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. In this article, we'll take a look at the symptoms, causes, and various treatment options to help you effectively treat plaque psoriasis.
Plaque psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disease characterized by the formation of red, raised, and scaly patches on the skin. These spots, also called plaques, can appear anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. In this article, we'll take a look at the symptoms, causes, and various treatment options to help you effectively treat plaque psoriasis.
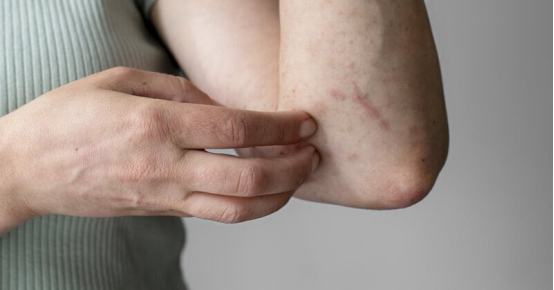
Plaque psoriasis has a range of symptoms that vary in severity from person to person. It's important to recognize these symptoms in order to seek appropriate treatment. The most common symptoms are:
It is important to note that plaque psoriasis is a chronic condition, which means that symptoms may come and go with periods of flare-ups and remissions.
The exact cause of plaque psoriasis is unknown, but researchers believe it is a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. Some of the key factors that contribute to the development of plaque psoriasis are:
Understanding the causes of plaque psoriasis can help patients manage and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Although there is currently no cure for plaque psoriasis, there are several treatment options that can manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve overall skin condition. Treatment plans are tailored to each person's specific needs and may include a combination of the following approaches:
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against plaque psoriasis. These medications are applied directly to the affected area and include:
Phototherapy involves exposing the affected skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial ultraviolet (UV) light. This treatment option can treat plaque psoriasis by slowing the overgrowth of skin cells. Phototherapy is usually performed in a medical setting under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
Systemic medications may be prescribed for people with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. These medications work internally to reduce inflammation and regulate the immune system. Common systemic treatments include:
In addition to medication, certain lifestyle changes can help treat plaque psoriasis and minimize flare-ups. This includes:
Plaque psoriasis can be a tricky disease to deal with, but with the right diagnosis, treatment plan, and lifestyle changes, patients can effectively manage and reduce its effects. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential to managing this chronic skin disease. Remember to consult your doctor to get a personalized plaque psoriasis treatment plan and enjoy improved skin health and quality of life. Life.