The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) causes a persistent deterioration of the immune system and poses a serious threat to advanced cancer and other life-threatening infections. The disease can be controlled with medication and treatment; however, there is still no complete cure. Here is some basic information about rashes caused by HIV infection.
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) causes a persistent deterioration of the immune system and poses a serious threat to advanced cancer and other life-threatening infections. The disease can be controlled with medication and treatment; however, there is still no complete cure. Here is some basic information about rashes caused by HIV infection.
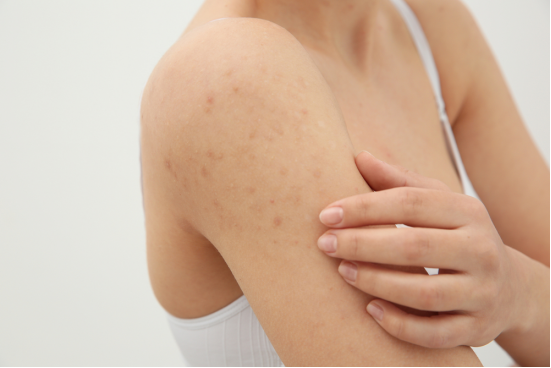
What is HIV rash?
- The most common and obvious symptoms of HIV infection include skin sores and rashes.
- These symptoms appear on the skin of HIV-infected people within two months of contracting HIV.
- The most common body parts where HIV-positive people develop rashes are the hands, legs, face, and chest.
- These rashes usually appear as flat, red spots with small bumps. People can look up pictures of HIV rashes online to determine if the rash is caused by HIV infection or something else.
- HIV rashes are accompanied by persistent itchy discomfort.
What causes HIV rash?
- HIV rash may appear on the skin of HIV-positive people as a symptom of the disease or as a side effect or allergic reaction to medications used to treat the disease, especially antiretroviral drugs.
- Therefore, the real reason for these rashes in HIV patients can never be proven.
What makes the rash worse?
Since the triggers of HIV rash may never be known, it is recommended not to make any lifestyle changes without consulting a doctor. Some factors that can make HIV rash worse include:
- Any type of allergic reaction, infection, or illness can make the skin condition worse in HIV-positive people.
- Certain medications.
- Direct sunlight on the skin can make HIV rash worse.
- Changes in eating habits or diet.
- Changing toiletries regularly.
- Exposure to extreme temperatures or hot showers.
What is seroconversion rash?
- Within a few weeks of contracting HIV, HIV antibodies begin to grow in the infected person's body and a rash and flu-like, swollen lymph nodes appear. This rash is called seroconversion rash.
- This rash does not cause itching and appears as flat red spots on the chest or back.
What is cellulite?
- Cellulitis is a rapidly spreading skin infection that occurs in the deepest layer of the skin and subsequently causes swelling, severe pain, and high fever.
- This condition usually starts with a small wound on the skin.
- However, the infection can also be caused without a wound.
- The infected area of cellulitis in HIV-infected people will feel hot to the touch due to inflammation of the skin.
- If the infection spreads quickly, red streaks extending from the main infection site may become visible.
What is herpes?
- Due to weaker immunity, HIV-positive people experience more severe herpes symptoms and illness than people who are not infected with HIV.
- Herpes appears as a rash and is a highly contagious skin infection.
- Herpes simplex type 1 and herpes simplex type 2 can cause blisters to appear in the mouth, genitals, or both.
- These blisters are painful and crust over.
- Herpes zoster, also known as shingles, occurs on only one side of the body; however, HIV-positive people may develop shingles on both sides of the body.
What is ringworm?
- One of the most common fungal infections that causes a rash is ringworm.
- HIV-positive people are very susceptible to infection.


